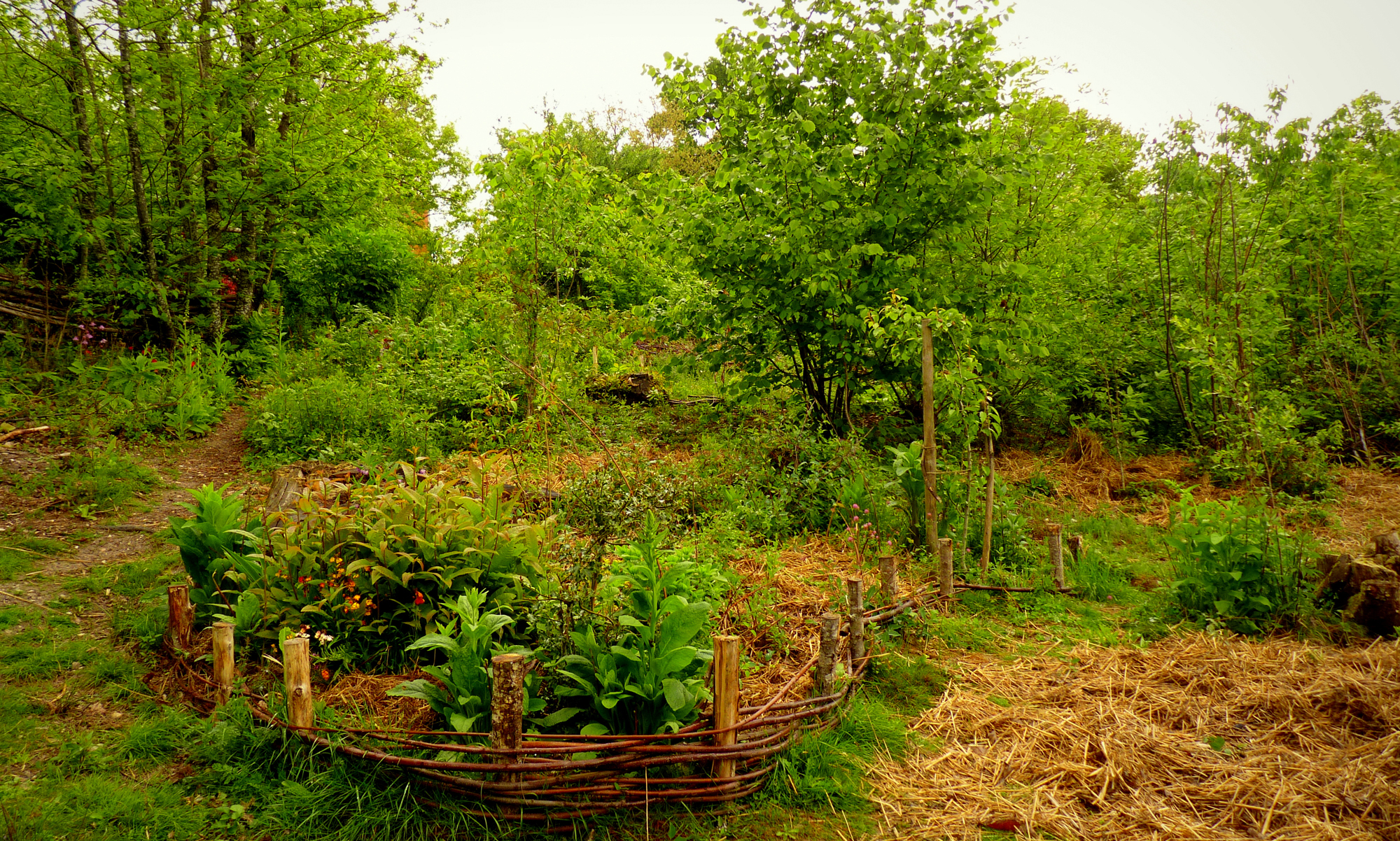
The conditions in mountain regions are often harsh and unaccommodating. However despite this, biodiversity urgently needs spreading throughout these regions so that mountain ecosystems can continue doing their work of regulating the global water cycle and climate.
It is not enough to simply plant trees, the biodiversity needs to be long-term sustainable. Therefore, in these conditions, man-made technological innovation is not enough. For this task it is necessary to work with the tried and tested strengths of nature. Nature has evolved and adapted in intricate ways to deal with extreme conditions. These strengths can be worked with by humanity to achieve positive and successful results. It is still conceivably possible to create an interconnected network of biodiversity throughout mountain regions. Green corridors linking community managed protected groves would be an ideal way of doing this. However because of the harsh conditions and urgency of the situation, it is necessary to work with the co-supporting properties of plant combinations that naturally exist within biodiversity.
Permaculture is a very effective and efficient approach for utilising the positive properties of plants.
“Permaculture shows how to observe the dynamics of natural ecosystems. We can apply this knowledge in designing constructed ecosystems that serve the needs of human populations without degrading our natural environment. Permaculture sites integrate plants, animals, landscapes, structures and humans into symbiotic systems where the products of one element serve the needs of another. Once established, a permaculture system can be maintained using a minimum of materials, energy and labor.”
Download: Sandy Cruz and Jerome Osentowski, Permaculture Article.pdf
Bill Mollison developed permaculture after spending decades in the rain forests and deserts of Australia studying ecosystems.
He observed that plants naturally group themselves in mutually beneficial communities and he used this idea to develop a different approach to agriculture and community design. It is based on the interdependent way that nature functions with the different plant and wildlife species regulating and supporting one another. Ideas for companion planting comes from similar observances.
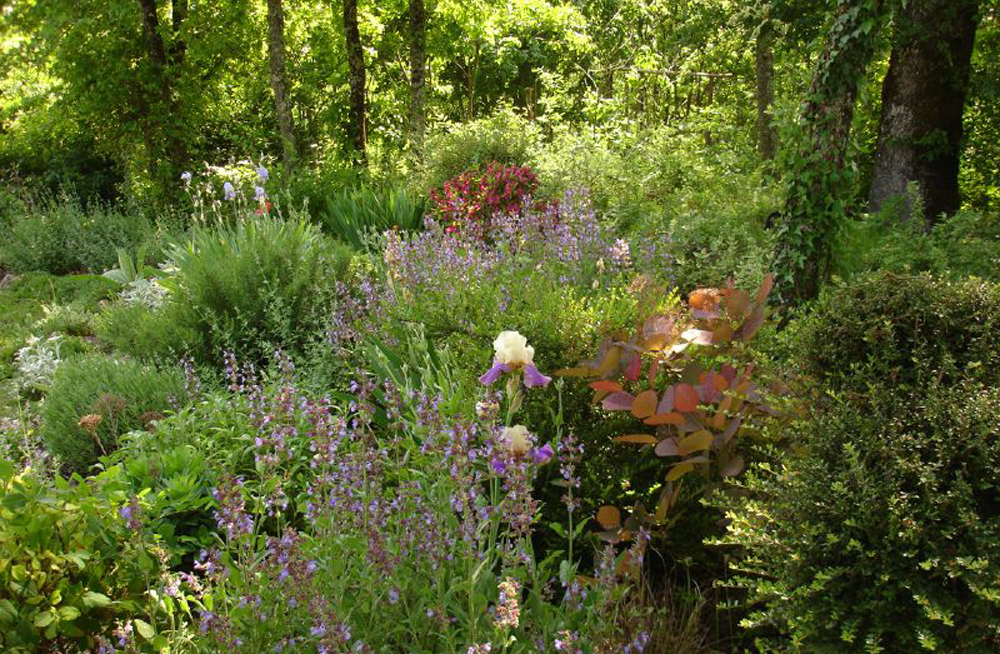

The word Permaculture refers to permanent agriculture and is understood as agriculture that is based on a natural sustainability model and that can be sustained indefinitely.
It also refers to permanent culture, which recognizes the profound relationship between humanity and the environment and an understanding of the supportive dynamics of varied ecosystems. It is an integrated design philosophy that encompasses gardening, architecture, horticulture, ecology, even money management and community design. The basic approach is to create sustainable systems that provide for their own needs and recycle their waste.
“Human beings are at the centre of concerns for sustainable development. They are entitled to a healthy and productive life in harmony with nature.”
Download: UNCED, Rio 1992, Principe 1, Report on UN Conference on Environment and Development.pdf
Living and working in a way that is in harmony with nature is a topic that has created a lot of discussion in recent times especially in the context of sustainable development.
Although the term ‘Permaculture’ is relatively recent, it draws upon thousands of years of traditional knowledge and human observance of the most beneficial natural dynamics and combinations that provide long-term environmental sustainability. It is a way of forest gardening and living in accord with nature and natural abundance, rather than being at odds, depleting and wasting nature’s vast store. This knowledge can be applied for protecting and restoring ecosystems and serving the needs of humanity without degrading natural environments. It is a way for humanity to work and live in harmony with Nature, which respects the rights of fellow humans along with the other species that one shares this vast Earth with.
Our proposed method takes into account long-term environmental sustainability, human rights, economies and the reduction of poverty and embraces the essence and principles of Sustainable Development as agreed upon by world governments in Agenda 21 in 1992.