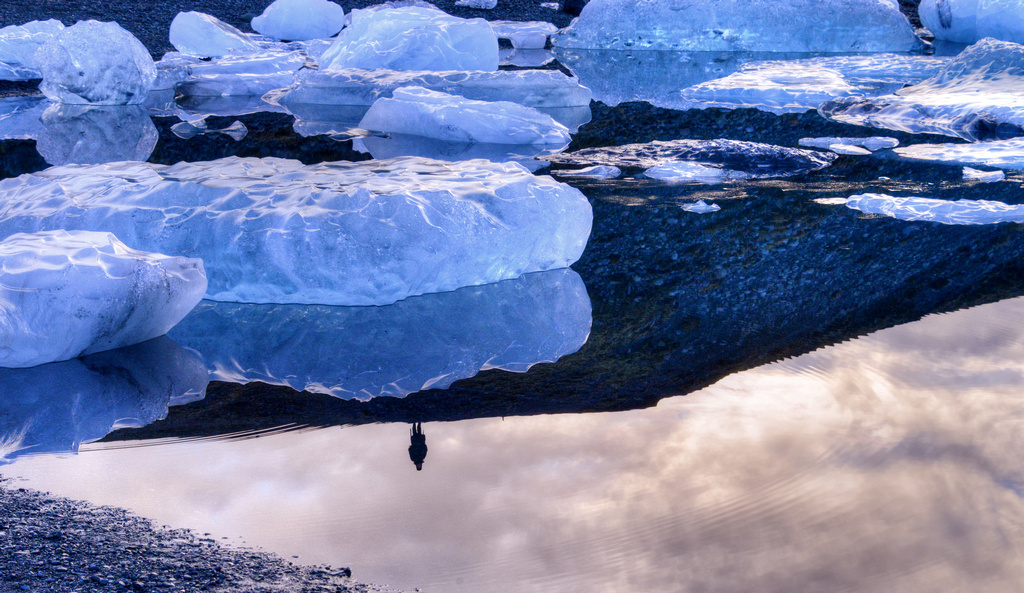
Glaciers are melting at an unprecedented rate worldwide and many major ones could vanish within the next fifty years.
“Today the shrinking of mountain glaciers is taking place at a global scale and at a rapid rate. The strikingly synchronous retreat in many parts of the world since the late 20th century may be unique; in many regions, glaciers have now been reduced close to their minimum extent during the climate optimums in the Holocene, i.e. in the past 10,000 years (Solomina et al 2008) – and in some places even beyond this.” Download: Mountains and Climate Change, Kohler T. et al, 2009.pdf
The rate at which they are melting, is threatening freshwater supplies and climate stability around the world and the process is escalating.
This worldwide scenario is becoming highly disturbing when we consider the implications for the global fresh water supply. All countries, rich and poor alike are threatened by this same looming water related crisis and all the consequences of it.
“If current trends continue, 75% of the glaciers in the Swiss Alps are likely to disappear by 2050” Download: Climate Change impacts on Mountain Regions of the World, UNESCO, 2013.pdf
With so many glaciers retreating worldwide and increasing freshwater shortages, there is no long-term sustainability in large hydro dams for energy production.
“At the global level, it is this ice stored in the top of the mountains in the major continents that become vital in maintaining the river flows.” (Bandyopadhyay, 1992)
In addition, the environmental damage that hydro dams cause, puts even more pressure onto valuable water resources and crucial mountain ecosystems. These ecosystems are too important to lose. The massive depletion and potential disappearance of mountain snows and glaciers worldwide is a threat that humanity should do everything possible to prevent from becoming a reality. The extreme melting of these glaciers not only indicates climate change, they exacerbate and accelerate climate change. The Earth’s mountain glaciers, permafrost, ice and snow acts as a protective mirror, reflecting a large percentage of the sun’s heat back into space and keeping the planet cool.
Their ability to reflect solar heat is one of many reasons why glaciers are crucially important in global climate regulation. As they melt and become thinner this function becomes less effective, greatly influencing rising temperatures upon Earth. This greatly exacerbates climatic instability worldwide.
“Most glaciologists believe we are witnessing unprecedented changes to land and sea ice. The burning question is not if, but how fast, land and sea ice will disappear, and what we can do to mitigate and adapt to these changes.” (Prof Jonathan Bamber Director of the Bristol Glaciology Centre)
Yet this massive loss is not something that can be adapted to. Rises in temperature above 1o C (J Hansen) could lead to a global climate catastrophe. Therefore the accelerating retreat of mountain glaciers must be slowed down.